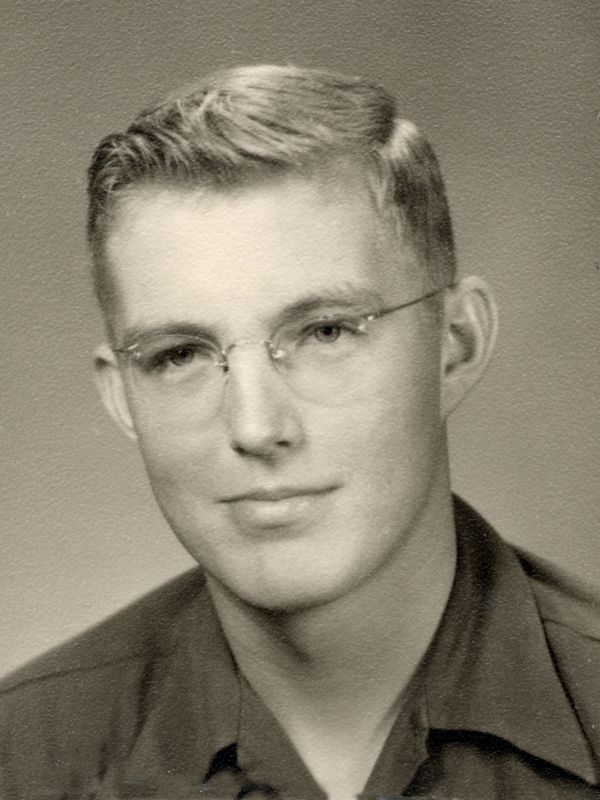
Canadian Bruce Wallace Dunn, responding to a question on his Wheaton College application regarding his choice for location after graduation, wrote, “California – otherwise no preference.” As it happened, Dunn’s career did not move him westward but straight south to Peoria, Illinois. As road-weary vaudevillians used to say, “If it’ll play in Peoria, it’ll play anywhere.” There Dunn’s fruitful ministry “played” for decades not because of chance, but as the result of, as he observed, “…many prayers, much planning, and sacrificial giving by hundreds of people.” Born to a godly family of Scottish heritage in Toronto, Ontario, Dunn was the first boy in Dr. Oswald Smith’s Sunday School class at the famous People’s Church. Regularly attending for years but still unsure of his beliefs, Dunn finally walked the aisle in 1936, publicly declaring his faith in Christ after hearing former hoodlum Anthony Zeoli testify to God’s grace.
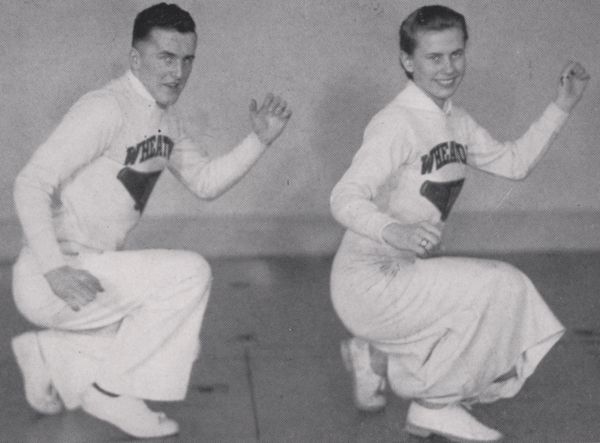 Offering his life to God, Dunn enrolled at Wheaton College where he robustly participated in campus life, involved with cheerleading, tennis, ping pong and the Aristonian Literary Society. In addition to sports, he reported for the Record, traveled with the Ambassadors (Wheaton’s musical evangelists) and served on the Men’s Interhouse Council. Earning his B.A. (’40) and M.A. (’46), he transferred to McCormick Seminary in Chicago and then Northern Baptist Theological Seminary, where he acquired his Th.D. After serving briefly in Iowa, Wisconsin and Chicago, Dunn in 1951 accepted a call to pastor at Grace Presbyterian in Peoria. A few months later he inaugurated a radio broadcast, later moving his congregation to a larger building and a successful television ministry called Grace Worship Hour. He enjoyed a national reputation as a powerful speaker, preaching for conferences like Moody Founder’s Week, Moody Keswick, Winona Lake, West Coast Prophetic Congress and many others. Specializing in prophetic interpretation, he stressed the need for continual evangelization.
Offering his life to God, Dunn enrolled at Wheaton College where he robustly participated in campus life, involved with cheerleading, tennis, ping pong and the Aristonian Literary Society. In addition to sports, he reported for the Record, traveled with the Ambassadors (Wheaton’s musical evangelists) and served on the Men’s Interhouse Council. Earning his B.A. (’40) and M.A. (’46), he transferred to McCormick Seminary in Chicago and then Northern Baptist Theological Seminary, where he acquired his Th.D. After serving briefly in Iowa, Wisconsin and Chicago, Dunn in 1951 accepted a call to pastor at Grace Presbyterian in Peoria. A few months later he inaugurated a radio broadcast, later moving his congregation to a larger building and a successful television ministry called Grace Worship Hour. He enjoyed a national reputation as a powerful speaker, preaching for conferences like Moody Founder’s Week, Moody Keswick, Winona Lake, West Coast Prophetic Congress and many others. Specializing in prophetic interpretation, he stressed the need for continual evangelization.
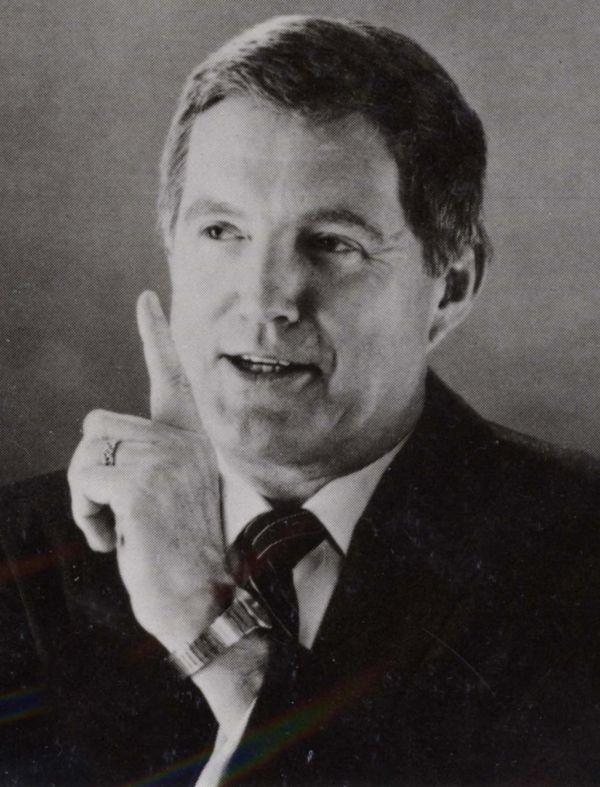
 Occasionally his sermons were published as pamphlets, such as The Ecumenical Dream…One Big Church!, reflecting his alarm over ill-considered ecclesiastical mergers and unions. In 1960 Wheaton College awarded him its Centennial Award for his uncompromising testimony; and in 1968 he delivered the Baccalaurate address for Taylor University. Dunn’s wife, Eileen, graduating summa cum laude from Wheaton College in 1947, was employed as a librarian at Bradley University for 25 years. She died in 1989, her graveside service occurring on the 48th anniversary of their wedding. Dr. Bruce Dunn retired from Grace Presbyterian in 1991, continuing with writing and periodic speaking engagements until his death in 1993. His funeral address was delivered at Grace Presbyterian Church by Dr. Joseph Stowell, president of Moody Bible Institute.
Occasionally his sermons were published as pamphlets, such as The Ecumenical Dream…One Big Church!, reflecting his alarm over ill-considered ecclesiastical mergers and unions. In 1960 Wheaton College awarded him its Centennial Award for his uncompromising testimony; and in 1968 he delivered the Baccalaurate address for Taylor University. Dunn’s wife, Eileen, graduating summa cum laude from Wheaton College in 1947, was employed as a librarian at Bradley University for 25 years. She died in 1989, her graveside service occurring on the 48th anniversary of their wedding. Dr. Bruce Dunn retired from Grace Presbyterian in 1991, continuing with writing and periodic speaking engagements until his death in 1993. His funeral address was delivered at Grace Presbyterian Church by Dr. Joseph Stowell, president of Moody Bible Institute.